The Cincinnati Kid
There are diseases that become forever associated with a famous victim. Michael J. Fox is active with research for Parkinson’s Disease. Mary Tyler Moore was a lifelong diabetic. Jerry Lewis, although not a victim of the disease, will always be associated with the marathon television fundraisers he organized and helmed for Muscular Dystrophy.
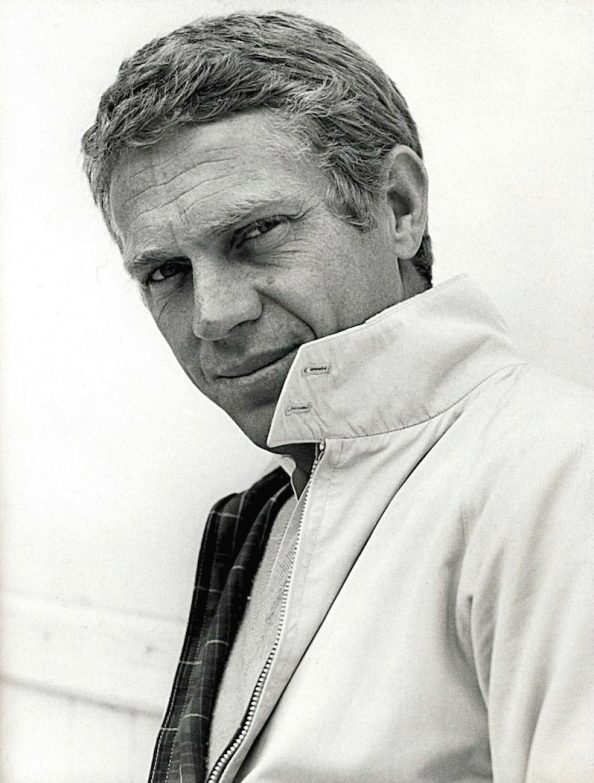
One particularly insidious disease had, as its most famous victim, Mr. Cool, himself – a man who once said, “You only go around once in life, and I’m going to grab a handful of it.” And, boy, did he ever!
 The Cincinnati Kid was at the top of Charles Manson’s “hit list.” It was by sheer luck that this A-list actor was not present the night Manson’s minions struck and killed Roman Polanski’s pregnant actress wife, Sharon Tate, and her entourage at her Los Angeles home. (After learning his name was on a Manson “hit list,” the star began carrying a gun.) His last words were said to be, “I did it,” although other reports say he died in his sleep under an assumed name (Sam Shepherd) at a Juarez, Mexico clinic. This mega-star died of mesothelioma – a cancer affecting the lining of the organs, such as the lungs, heart and/or abdomen.
The Cincinnati Kid was at the top of Charles Manson’s “hit list.” It was by sheer luck that this A-list actor was not present the night Manson’s minions struck and killed Roman Polanski’s pregnant actress wife, Sharon Tate, and her entourage at her Los Angeles home. (After learning his name was on a Manson “hit list,” the star began carrying a gun.) His last words were said to be, “I did it,” although other reports say he died in his sleep under an assumed name (Sam Shepherd) at a Juarez, Mexico clinic. This mega-star died of mesothelioma – a cancer affecting the lining of the organs, such as the lungs, heart and/or abdomen.
Who was he? The Cincinnati Kid? More about that in a moment.
Mesothelioma is a disease that kills between 2,000 and 3,000 people annually, and an estimated 43,000 people around the world die from the disease each year. You can be exposed to the asbestos, which is a known cause of the illness, and not show any symptoms for decades due to the disease’s long latency period. It is particularly difficult to catch early, because the symptoms mimic so many others. To wit:
- Shortness of breath, wheezing or hoarseness
- A persistent cough that worsens
- Blood coughed up from the lungs
- Pain or tightness in the chest
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swelling of the neck or face
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fatigue or anemia
Those symptoms mimic many other diseases, and victims often do not seek help until their illness is too far advanced for effective treatment. Even cases that are caught early have a grim prognosis.
 One other famous face of mesothelioma was musician Warren Zevon, who wrote “I’ll Sleep When I’m Dead.” In a “Tonight Show” program devoted solely to Zevon and his music, talk show host David Letterman paid tribute to the “Werewolves of London” tunesmith. Zevon advised, known to be terminal with mesothelioma at the time of the taping, advised others “enjoy every sandwich.” (These taped appearances can still be found on YouTube and are deeply moving; Zevon worked right up until his death, compiling a memorable final album which featured many guest artists.)
One other famous face of mesothelioma was musician Warren Zevon, who wrote “I’ll Sleep When I’m Dead.” In a “Tonight Show” program devoted solely to Zevon and his music, talk show host David Letterman paid tribute to the “Werewolves of London” tunesmith. Zevon advised, known to be terminal with mesothelioma at the time of the taping, advised others “enjoy every sandwich.” (These taped appearances can still be found on YouTube and are deeply moving; Zevon worked right up until his death, compiling a memorable final album which featured many guest artists.)
The famous face of mesothelioma mentioned in paragraph two has been named one of the Top Thirty Movie Stars of All Time on various polls. His work has been cited as an influence on actors working today, like Bruce Willis and Colin Farrell. He once said, “I live for myself, and I answer to nobody.” That maverick anti-establishment attitude informed his work and his life—and made it more difficult to get him to consult a doctor when he first noticed a persistent cough in 1978. Although he gave up his cigarette habit and underwent antibiotic treatments, he did not improve.
Finally, after filming one of his final films, “The Hunter,” “The Cincinnati Kid”, Steve McQueen had a chest X-ray and a biopsy. The biopsy revealed pleural mesothelioma, an aggressive and rare cancer directly caused by exposure to asbestos. The most likely explanation for why McQueen contracted the disease is also in keeping with his rogue image: he was a Marine at one point early in life and was sent to the brig for not reporting for duty, but being absent without leave (AWOL) to spend time with a woman. Part of McQueen’s punishment was to remove asbestos from pipes aboard a troop ship.
McQueen also speculated that Hollywood’s love affair with asbestos, which was used on movie sets to create fake snow from 1930 to 1950, might have exposed him to the deadly carcinogen. The use of asbestos occurred in movies as famous as the Bond film “Goldfinger” and “It’s A Wonderful Life” (although not used in that Jimmy Stewart picture as snow, because a substance known as foamite had been invented for that purpose in 1946). Asbestos was used to decorate other parts of the “It’s A Wonderful Life” set and it was used in the CBS Network facilities building for years, where another veteran character actor, Ed Lauter (“The Longest Yard,” “The Family Plot”), worked for many years. He died of the disease in 2013 at the age of 75, only five months after his diagnosis.
In 1942, when Bing Crosby sang “I’m Dreaming of a White Christmas” in the film “Holiday Inn,” the snow falling was actually asbestos, and 1939’s “Wizard of Oz” relied on asbestos for the poppy field scene. Stunt men who wore flame retardant suits in films were exposed to asbestos (McQueen did many of his stunts himself and “Towering Inferno” was one of his biggest films) The suits that race car drivers often wore contained asbestos in the early days; McQueen was a well-known racing enthusiast of both fast cars and motorcycles.
Steve McQueen’s efforts to find treatment led him to Mexico to undergo questionable treatments by a man (William Donald Kelley) who promoted a version of the Gerson therapy. It used coffee enemas, daily injections of fluid containing live cells from cattle and sheep, massages, frequent washing with shampoos, and laetrile, which is derived from apricot pits. Nothing worked. McQueen paid upwards of $40,000 a month ($116,000 in today’s dollars) for the treatments over three months in Mexico. (Kelley’s medical license was revoked in 1976).
Against his U.S. doctor’s advice (doctors in the U.S. said his heart was too weak), Steve McQueen underwent surgery to remove huge tumors that had, by that time, spread to his liver, neck and abdomen. [The liver tumor, alone, allegedly weighed five pounds] McQueen died of cardiac arrest at 3:45 a.m., twelve hours after surgery on November 7, 1980, at age 50. The El Paso Times said he died in his sleep. He was cremated and his ashes were spread over the Pacific Ocean.
Meanwhile, the asbestos that took Steve McQueen’s life at age 50, almost 40 years ago, is still legal in the United States. First responders to the 9/11 attack in New York City on September 11, 2001, survivors present in the city and those involved in cleanup at the site were exposed to asbestos, as it was used in the construction of the North Tower of the World Trade Center. Hundreds of tons of asbestos was released into the atmosphere as a result of the airplane attacks. My own nephew, an architect, was in charge of plans by an architecture firm to remove asbestos from schools in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, that took place within the last five years.
Organizations like the Mesothelioma Cancer Alliance work year-round to educate people about the dangers of asbestos. Steve McQueen’s death was only one of thousands that year, but people are still being exposed to the mineral today and thousands will be diagnosed this year.
Maybe it’s time to step up and make asbestos illegal in the United States?
The Cincinnati Kid